
JIQ conversational platform is a multitech tool. Each technology works independently and provides reliable work of the inner architecture.
The core of the virtual agent technology is the dialog engine, which understands what to answer the customer, depending on the conversation context. The dialogue engine is based on a pre-rendered script. We use many complex neural network models to make a voice agent sound human-like.
Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
With the evolving of speech signal processing techniques, the need to detect the speech presence in the incoming signal under different noise environments has become one of the industry main goals. It is achieved using Voice Activity Detectors (VAD).
VAD separates a speech signal from other background sounds, such as ambient noise or music. It helps us reduce the load on the speech recognizer and prevent false positives for sounds similar to a human voice, for example, birdsong or some musical instruments.
Answering Machine Detection (AMD)
Imagine a situation when a voice assistant reached your customer and heard an answering machine. Will such interaction be effective? Obviously, not. Therefore, JIQ provides a three-level auto-responder detection system.
The first level occurs when dialing the customer. A special model analyzes the presence of beeps in the audio signal from the establishing connection until the phone call is answered.
The second stage identifies intelligent answering machines and uses the speaker verification method. This is a neural network model trained on a large dataset consisting of several tens of thousands of voices.
The third level of defining autoresponders applies the NLU model to define the appropriate intents.
Speech-to-Text (STT)
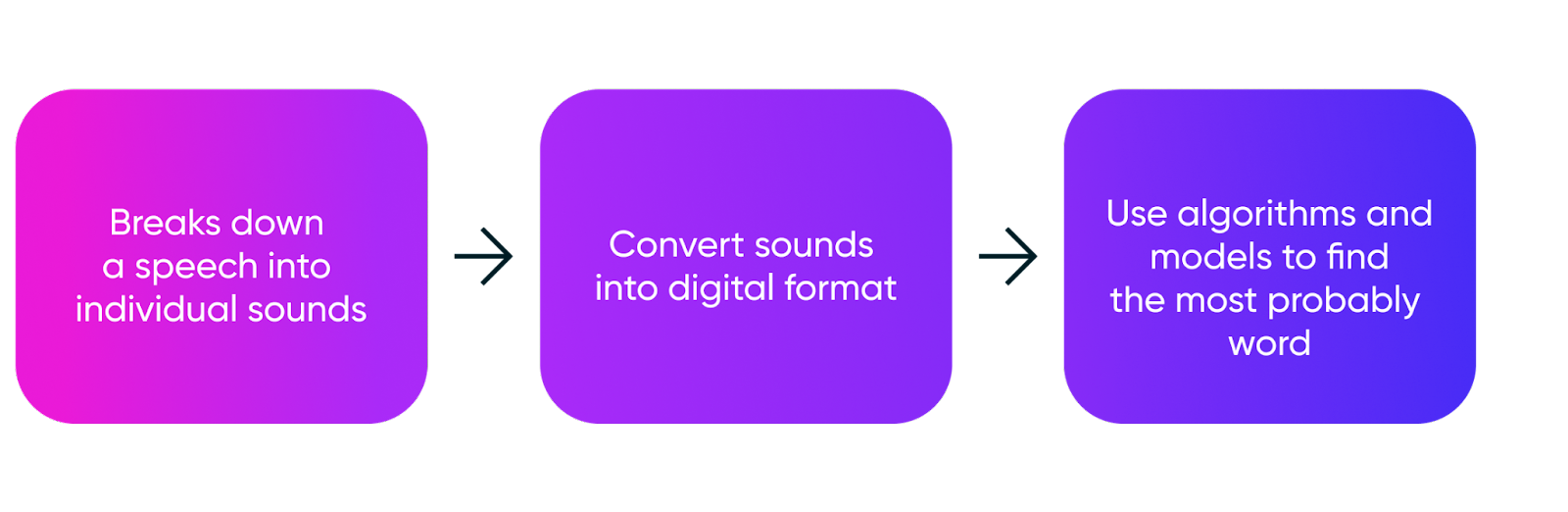
The Speech-To-Text (STT) technology finds the most probable sequence of words in the audio.
A voice has to go through many distinct steps before a computer can determine what was said.
First, a microphone has to convert out speech into a digital input, which a computer attempts to classify into a recognizable sound using statistical models and neural networks.
Then words and phrases are picked out by analyzing these sounds until the correct phrase is determined.
We use the E2E model that supports the recognition of 13 common European languages.
Natural Language Processing (NLU, Semantic Similarity Search, and GPT3)
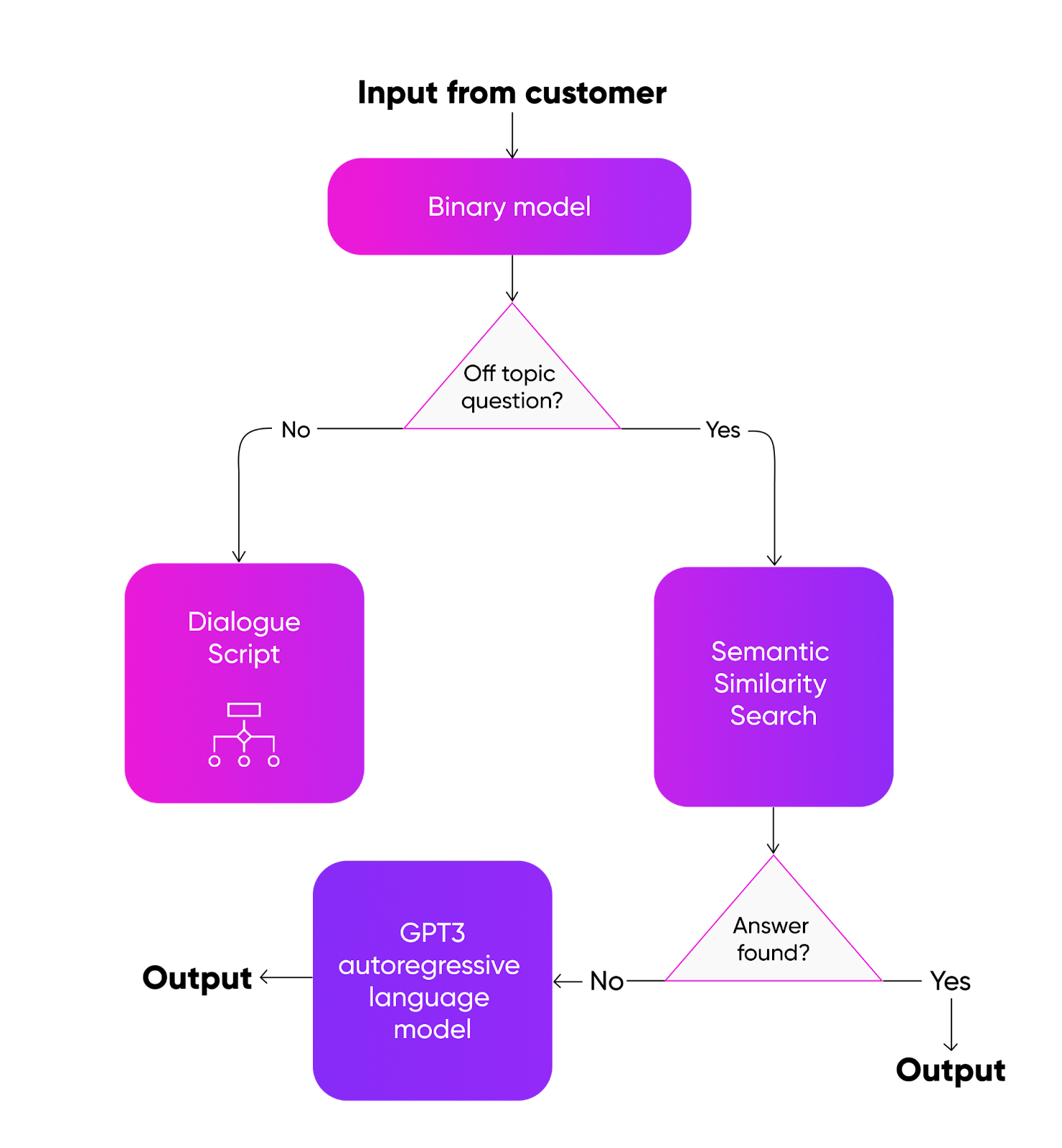
After converting the speech into text, we need to understand what type of phrase we received. Is it consent? A question on the price? Perhaps the terms of use? Or the amount of the interest rate? Such classification is handled by the NLU - Natural Language Understanding module.
On the first step, we use a binary model to separate the target phrase from the non-target one. In other words, it can distinguish "How many years have you been driving?" from “How many years will I have to repay the loan?” If the phrase is defined as a target, then the voice agent uses the script to select the answer.
If the question was non-targeted, the voice agent accessed a prepared knowledge base of questions and answers. The task of this stage is to find the most similar question and provide a pre-prepared reply. This knowledge base covers all the Mobile Assistant's interests, work, and hobbies, making it feel like you're talking to a human, not a robot.
Also, the assistant can be asked about some facts, for example, “Does Charles III have a passport?”, the voice agent goes to the third stage - a generative model trained on the entire English Wikipedia.
Dialogue Manager (DM)
When the AI understands a phrase's meaning, it turns to the Dialog Manager (DM). Its main task is to choose the best answer depending on the context and a given phrase. Depending on the settings at each step, the DM can:
- Issue a response according to the script;
- Reach external systems for missing data (for example, the amount of the account balance);
- Capture or send a formalized customer response to the client's external system (for example, the specified delivery address).
Voice Interruption Detector (VID)
Voice Interruption Detector (VID) is needed to maintain a comfortable dialogue between the customer and the voice agent and respond to simultaneous speech in different ways:
- Stop talking immediately;
- Finish the sentence;
- Ask the customer to allow finishing.
Emotional Text-to-Speech (STT)
After the best answer is found, the virtual agent can voice it using pre-recording or with the help of a speech synthesis module. Sometimes a combination of both options is used. JIQ Conversational AI Platform allows you to create a digital copy of any voice, so our clients can receive a unique synthesized voice and make it part of their brand.
Get JIQ Voice Agent to scale your business
JIQ Conversational AI Platform provides Voice Assistants powered by a unique combination of disruptive technologies to make customer interactions more efficient and satisfying.







